The Evolution of MPLS and Its Impact on Modern Networks
What Is MPLS?
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a sophisticated technique for optimizing data traffic management across complex networks. MPLS uses short path labels rather than relying on traditional IP routing, which requires examining the lengthy network addresses at each hop. These labels mark the data packets, allowing them to be swiftly directed to their destinations. This significantly reduces processing overhead and increases the efficiency of data transfer. Multiprotocol label switching acts as a streamlined route for your data. It is akin to an express highway bypassing the slower surface roads, ensuring that information gets where it needs to go quickly and reliably.
Businesses benefit immensely from implementing MPLS. Whether it’s enhancing the performance of critical applications or ensuring smoother communication across geographically dispersed offices, MPLS proves its worth. However, understanding the underlying mechanics helps to appreciate its full range of advantages and how it differs from other network technologies.
Benefits of MPLS
- Increased Reliability: MPLS creates more stable network connections less prone to disruptions. This reliability is crucial for operations that require consistent uptime and performance, such as financial services and healthcare operations.
- Enhanced Speed: MPLS allows data to travel faster by reducing the number of hops and the time it takes to identify packet routes. This speed boost can significantly improve user experience and application effectiveness.
- Better Bandwidth Management: MPLS allows for efficient bandwidth allocation, which can prioritize critical business applications over less important traffic. This optimized bandwidth use ensures that key processes remain unaffected during peak usage times.
It provides a detailed examination of MPLS’s benefits, which provides additional insights into how MPLS can improve network performance for various applications.
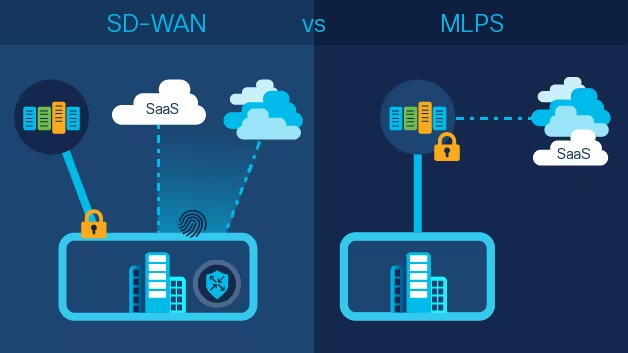
MPLS vs. SD-WAN
While MPLS has dominated network management for many years, emerging technologies such as Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN) have introduced new possibilities. SD-WAN offers greater flexibility, which is particularly useful for businesses with extensive cloud-based activities and distributed networks. It allows multiple forms of connectivity—including broadband internet—to manage traffic, giving businesses the agility to adapt to ever-changing demands.
However, MPLS still holds an edge in environments that require unwavering stability and guaranteed performance. Unlike SD-WAN, MPLS provides consistent, predictable service levels, making it indispensable for mission-critical applications where even minor disruptions can have significant repercussions. The decision between MPLS and SD-WAN often boils down to whether stability or flexibility is the primary concern for the business.
MPLS Security Considerations
Due to its inherent design, MPLS presents distinct advantages in terms of security. Unlike public internet connections, which are open and vulnerable to attacks, MPLS networks isolate data traffic from the public domain. This isolation significantly reduces exposure to potential threats. However, MPLS does not encrypt data by default, so additional security measures are often necessary.
Businesses often add additional security measures, like Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and advanced firewalls, to enhance the protection of their data. These extra precautions guarantee that in the event of data interception, it would be challenging to decrypt, which helps keep sensitive information confidential and intact. It is essential for businesses to comprehend these security dynamics in order to make well-informed decisions regarding their network infrastructure.
The Future of MPLS
Despite the advent of newer networking technologies, MPLS is not fading into obsolescence. Continuous innovations are enhancing its capabilities, making it adaptable to modern demands. Hybrid models that combine MPLS with SD-WAN are gaining traction, providing businesses with the reliability of MPLS and the agility of SD-WAN. These hybrid solutions offer a balanced approach, ensuring robust connectivity while accommodating the dynamic nature of contemporary network requirements.
As businesses increasingly adopt cloud services and require flexible networking solutions, the future of MPLS lies in its integration with these adaptable technologies. This evolution ensures that MPLS remains relevant and valuable, addressing current and emerging network challenges.
Real-World Use Cases
- Financial Institutions: The financial sector relies heavily on MPLS for secure and reliable transaction processing. High-frequency trading, for instance, demands low latency and high reliability—attributes that MPLS delivers effectively.
- Healthcare Providers: In healthcare, the integrity and confidentiality of patient data are paramount. MPLS supports these requirements by providing stable connections for data transfer and access, ensuring sensitive information remains protected during transmission.
- Retail Chains: Retail operations benefit from MPLS by supporting consistent point-of-sale transactions across multiple locations. This consistency ensures that sales data is accurately captured and transmitted, facilitating seamless business operations and inventory management.
Challenges and Limitations
While MPLS offers numerous benefits, it has challenges. The cost associated with deploying and maintaining an MPLS network can be prohibitive, particularly for smaller businesses. Furthermore, scalability is another issue; expanding an MPLS network often necessitates significant investments in infrastructure, which can be a limiting factor for growing companies.
Moreover, the rigidity of MPLS makes it less suited for dynamic, rapidly changing networking environments. Unlike SD-WAN, which can quickly adapt to fluctuating connectivity needs, MPLS tends to be more static, preferring established routes and configurations.
Conclusion
MPLS remains a cornerstone in network management, offering unparalleled reliability and efficiency. Its proven ability to provide consistent, high-quality service makes it invaluable for businesses where network performance is critical. As the landscape of business technology evolves, the hybrid integration of MPLS with solutions like SD-WAN provides an optimal approach to meeting contemporary networking demands.
Understanding MPLS’s strengths, limitations, and prospects is essential for making informed decisions about network infrastructure. As new challenges and opportunities arise, MPLS, with its established reliability and ongoing innovations, continues to be a relevant and valuable component in the ever-evolving world of network management.