How Telehealth is Transforming Modern Healthcare
Introduction to Telehealth
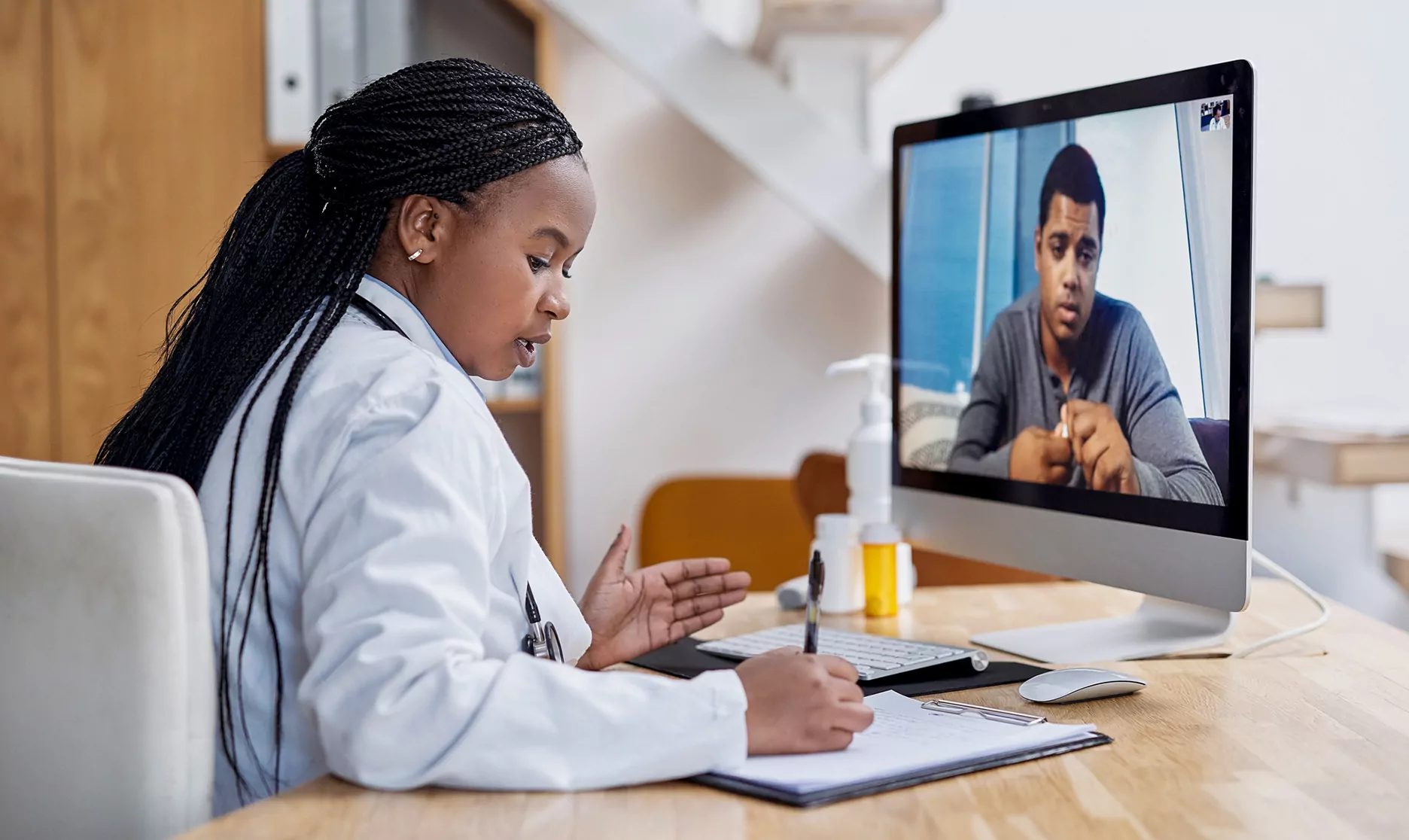
Telehealth has been seen as an innovative healthcare option, giving patients the opportunity to seek medical advice from their own residences. This mode of healthcare delivery leverages digital technology to facilitate virtual medical consultations, diagnostics, and treatments.
The COVID-19 pandemic has exponentially increased the adoption of telehealth services, making it an integral part of modern healthcare. With the need for social distancing and the strain on healthcare systems, telehealth provided a critical means to manage patient care without requiring physical presence. This shift not only improved accessibility but also equipped healthcare systems with the tools needed to deliver timely medical assistance, even during crises.
Key Benefits of Telehealth
- Accessibility: Ensures that individuals in remote or underserved areas receive medical attention. This is particularly important for patients with mobility issues or those living in regions with a scarcity of healthcare facilities.
- Convenience: Reduces the need for travel and waiting times. Patients can schedule appointments and receive care from the comfort of their homes, avoiding the hassle and potential stress associated with in-person visits.
- Cost-Effective: Lowers healthcare costs by reducing hospital readmissions and unnecessary ER visits. Telehealth can also decrease overhead costs for healthcare providers, making it a financially viable option.
- Improved Patient Engagement: Enables continuous monitoring and follow-up care. Tools such as patient portals and mobile health apps allow patients to stay engaged in their care, track their progress, and communicate easily with their healthcare providers.
According to a study by Johns Hopkins University, telehealth significantly improves patient outcomes because it provides timely and consistent care. One of the key elements driving this revolution is the availability of comprehensive telehealth solutions that ensure seamless and effective virtual care. This study highlights that patients who utilize telehealth services experience better management of chronic conditions and a higher rate of adherence to treatment plans. For additional insights, see this comprehensive report.
Technological Innovations Driving Telehealth
Advancements in technology are pivotal to the success of telehealth. Innovations such as high-speed internet, mobile health apps, and wearable medical devices have expanded the capabilities of remote healthcare. These technologies enable real-time data exchange, crucial for accurate diagnostics and effective treatment planning. High-speed internet connections provide the bandwidth for high-quality video consultations, ensuring clear communication between patients and providers.
Moreover, integration with electronic health records (EHRs) ensures that patient information is seamlessly accessible to healthcare providers. This integration allows for coordinated care, where multiple healthcare providers can manage a patient’s health collaboratively. For instance, a primary care physician, a specialist, and a nutritionist can all access duplicate patient records, making it easier to deliver comprehensive and cohesive care.
Telehealth in Rural Areas
Telehealth has had a profound impact on rural healthcare. In regions with scarce healthcare facilities, telehealth provides a lifeline, ensuring that residents receive necessary medical services. Through virtual consultations, patients in rural areas can connect with specialists who may be hundreds of miles away, thus bridging the healthcare accessibility gap. This is critical for conditions that require specialist care, which might not be available locally.
Another study published by the National Institutes of Health highlights that telehealth has drastically reduced emergency room visits in rural areas. The study found that telehealth services have helped manage chronic conditions more effectively, reducing the need for emergency interventions. For detailed information, refer to this informative article.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its numerous benefits, telehealth faces several challenges. These include data security, patient privacy, and technological barriers such as internet connectivity in remote regions. Ensuring the security of patient data is paramount, as breaches can compromise sensitive health information. Robust encryption and secure communication protocols are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Additionally, regulatory hurdles and reimbursement policies vary from state to state, making widespread adoption more complex. Healthcare providers must navigate a patchwork of regulations to provide telehealth services, which can be burdensome. Furthermore, reimbursement rates for telehealth services can differ significantly, impacting the financial viability of providers offering these services.
Future Trends in Telehealth
The future of telehealth looks promising, with the potential for more sophisticated AI-driven diagnostic tools, virtual reality consultations, and enhanced patient data analytics. These advancements are expected to make telehealth even more efficient and widely accessible, further revolutionizing the healthcare industry. AI-powered tools can assist in diagnosing conditions, predicting patient outcomes, personalizing treatment plans, and enhancing the quality of care.
Furthermore, as telehealth evolves, it will likely become an integral component of standard healthcare delivery, complementing traditional in-person visits. Integrating telehealth with other healthcare technologies will offer a more holistic approach to patient care. For example, combining telehealth with remote patient monitoring devices can provide real-time patient health data, allowing for proactive management of chronic conditions.
Real-World Examples
Several healthcare providers have successfully integrated telehealth into their service offerings. These real-world examples demonstrate the efficacy of telehealth in improving patient care, enhancing accessibility, and reducing costs.
- Example 1: A small rural clinic in Idaho reduced patient travel costs significantly by implementing a telehealth system for routine follow-ups and consultations. Patients who would typically have to travel long distances for a 15-minute appointment can now consult with their healthcare providers virtually, saving time and money.
- Example 2: During the COVID-19 pandemic, a large hospital in New York City utilized telehealth to manage non-critical patients, thus freeing up hospital resources for more severe cases. This allowed the hospital to triage effectively, ensuring that critical care resources were available for those who most needed them.